The agency is pushing for the approval of Mpox vaccines by all African Union member states, emphasizing the urgency amid global vaccine shortages. Dr. Jean Kaseya, the Director-General of Africa CDC, highlighted this in a letter addressed to the Ministers of Health of the African Union. The letter, titled “Update on the Mpox Outbreak in Africa,” calls for a coordinated response among the member states and the universal introduction of Mpox vaccines across the continent.
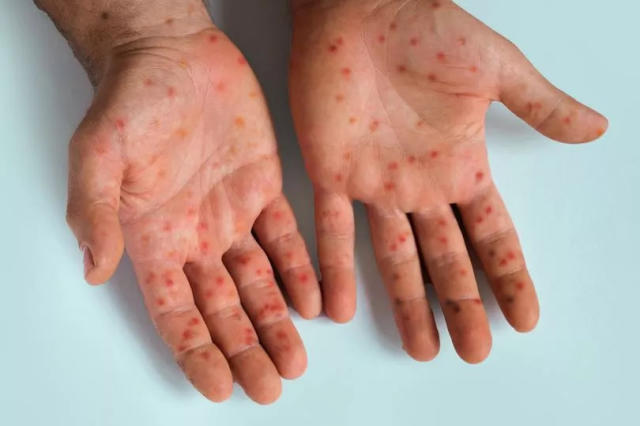
From 2023 to the present, Mpox has been reported in 16 African Union Member States across all five regions, with a high fatality rate exceeding 3.9 percent. Between January 1, 2024, and August 23, 2024, a total of 21,466 cases (3,350 confirmed and 18,116 suspected) and 591 deaths, with a case fatality rate of 2.9 percent, have been reported in 13 African Union Member States. The affected countries include Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Gabon, Liberia, Kenya, Rwanda, South Africa, Uganda, and Nigeria.
Dr. Kaseya noted that Gabon had confirmed its first Mpox case, while Sierra Leone and Malawi are currently testing suspected cases. Addressing concerns from Member States regarding lab-confirmed Mpox cases, Dr. Kaseya emphasized that relying solely on laboratory test results may not be sufficient to diagnose Mpox accurately. He consulted with top epidemiology and lab experts, including international bodies like the US CDC, China CDC, Europe CDC, and the World Health Organization (WHO), to provide better guidance.
Dr. Kaseya stressed that a negative lab test does not necessarily mean the absence of a Mpox epidemic. A holistic approach is required, integrating lab testing with clinical assessments and epidemiological data. Accurate diagnosis and management of Mpox should consider multiple factors, including clinical symptoms, epidemiological context, patient history, and risk factors.
Testing for Mpox can sometimes yield false negatives, particularly if the sample is taken too early or too late during the infection. Critical symptoms such as fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, and lesions should guide clinical examinations, especially when lab results are inconclusive. Understanding the patient’s exposure history, such as contact with known cases or travel to areas with ongoing outbreaks, is essential for identifying probable cases, even in the absence of positive lab results.
Dr. Kaseya also highlighted the importance of considering other factors such as viral variability and the potential for different strains or mutations of the Mpox virus that might not be easily detected by certain tests. Additionally, in some cases, an individual’s immune system might suppress the virus to undetectable levels, even though the disease is present.
He noted that only Nigeria, South Africa, and the Democratic Republic of Congo have approved the use of Mpox vaccines. Dr. Kaseya urged other African countries to follow suit, especially given the growing global demand for the vaccines and the risk that Africa might be overlooked in vaccine distribution if leaders do not take a unified stance.
The Director-General also warned that if African leaders and communities do not take the Mpox outbreak seriously, there is a risk that Western countries might impose travel restrictions on Africa. He mentioned that efforts are underway to raise public awareness and encourage vaccine use in affected countries, with support being provided through vaccine donations.
Dr. Kaseya concluded by addressing the complexities around vaccine access, noting that while availability is limited, the benefits of an expensive vaccine with limited clinical efficacy data need careful assessment. He called for plans to ensure that vaccines are effectively deployed to maximize their benefit, including securing regulatory approvals, ensuring proper supply chain logistics, and conducting communication campaigns to promote vaccine acceptance among the target populations.
For more updates, join our WhatsApp channel here.